Definition
The term equilibrium price refers to a state in which the quantity of goods supplied is equal to the demand for the same goods. Prices are typically stable for a product when they reach the equilibrium price.
Explanation
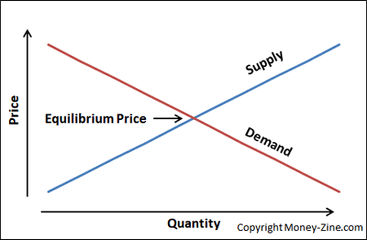
The equilibrium price is found at the point where demand for a product or service is exactly equal to supply. When supply and demand are plotted against price and quantity, the equilibrium price is found at the point where the supply curve intersects with the demand curve. Market forces will tend to bring supply and demand into balance; resulting in the following three generalizations:
When supply of a product or service is greater than demand, there is downward pressure on the price of the product or service.
When demand for a product or service is greater than supply, there is upward pressure on the price of the product or service.
When supply and demand for a product or service are in balance at the equilibrium point, the price of the product or service will be relatively stable.
Example
The following illustration demonstrates the equilibrium price.