Definition
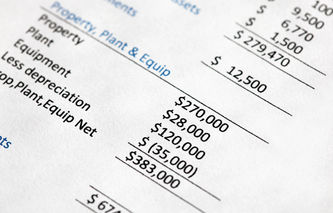
The term acquisition cost refers to the total of all the expenses associated with placing an asset into service. Acquisition cost is a managerial concept believed to more accurately reflect the total resources related to the purchase of an asset.
Explanation
Also referred to as the total cost of acquisition (TCA), acquisition cost is a managerial accounting concept that allows analysts to understand all of the resources associated with placing an asset into service. Acquisition cost would include both the factors that lower costs as well as those that increase it. For example, a company might acquire an asset for $1 million, but if the invoice is paid in less than thirty days, a discount of 5% might apply. The total cost of acquisition includes both incentives as well as discounts.
In the same way, TCA includes additional costs too. For example, expert services may be required to configure or tune a machine so it operates properly. It will also include any costs associated with shipping the asset to the company location, preparing the location to accommodate the asset, as well as the costs associated with installing it.