Definition
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid, or FAFSA, is a standardized financial aid document that ensures students seeking an education beyond high school are provided with the benefits they deserve under federally-funded programs.
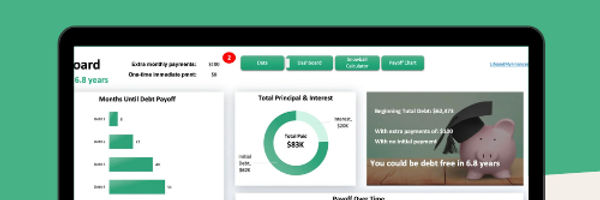
Ready to tackle your student debt? This student debt snowball spreadsheet is what you need!
A few key features of this template:
Proven method tailored to student loans
Customizable to YOUR needs
Works with Excel and Google Sheets
Can handle up to 32 debts!
Explanation
To apply for federal aid, as well as many state financial aid programs, students must first complete a Free Application for Federal Student Aid or FAFSA. Administered by an office of the U.S. Department of Education, the FAFSA is used to apply for federal student financial aid, such as grants, loans, and work-study. In addition, most states and schools use information from the Free Application for Federal Student Aid to award non-federal aid.
The Federal Student Aid office not only processes these applications, but also helps educate families on the process of obtaining financial aid. Once a loan is obtained, this agency also helps students during the repayment process, which is known as servicing a loan.
Completing a FAFSA is the first step in obtaining aid; the end-to-end process is summarized below:
Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA): application for student aid
Student Aid Report: validation of information appearing on the FAFSA
Expected Family Contribution: quantification of the student's share of college expenses
Award Letter: offer of student aid from the financial aid office of the educational institution
The Student Aid Report, or SAR, is available through the mail or the Internet. The SAR lists the information found on the FAFSA, and will provide an estimate of the Expected Family Contribution or EFC. Once verified, the EFC is used by the school's financial aid office to create an offer of aid for the student.



.jpg)
.jpg)